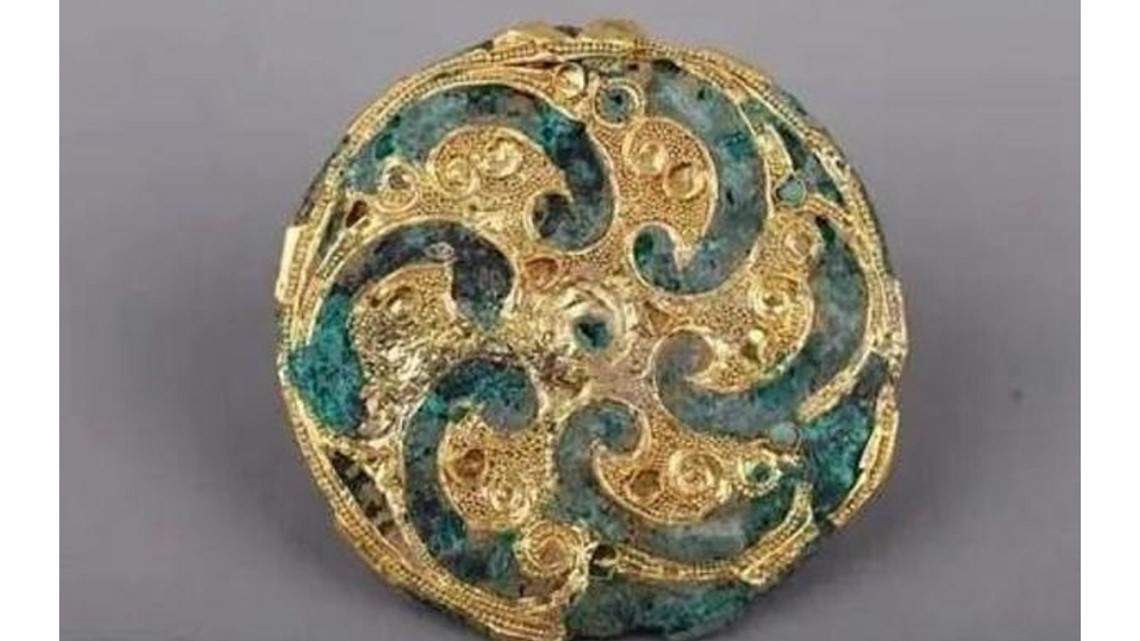
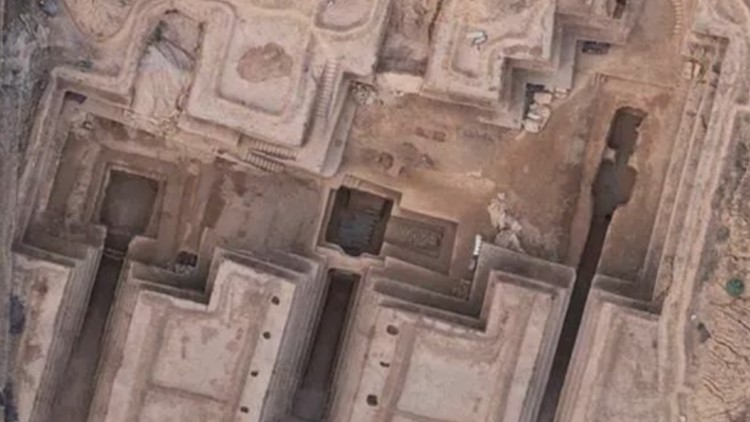
SHUN ZHUANG CUN, Wujin District — Archaeologists exploring a small village in China announced recently that they discovered three tombs filled with ancient treasures, including gold ornaments, a jade sword and ivory lacquerware.
The tombs are actually a "high-level family cemetery" from the Wei and Jin dynasties, a period of time from 220 A.D. to 589 A.D., experts said. These are the first such tombs found in the Shunzhuang Village, in China's Eastern Mengjin district, according to a news release about the discovery.
The tombs are large, and one was determined to be the second-largest tomb from this time period found in the area, second only to the imperial mausoleum in Luoyang, a nearby city. That tomb has multiple chambers and passages, while the other two tombs are smaller in size. The architecture of the tombs is still being studied by archaeologists.


The three tombs have been robbed "many times," according to the news release, but still contained treasures including gold ornaments, pottery, coins and more. There were over 200 artifacts found overall, according to the news release, including ivory lacquerware that had never been seen before. Those items are believed to be high-end crafts or practical items, and are "symbols of status" showing the wealth and power of the family in the tomb.
Archaeologists also found bone earrings, which are "relatively rare," with phoenix and bird patterns, and jade objects including a sword and belt hook. Those jade items are believed to be family heirlooms.

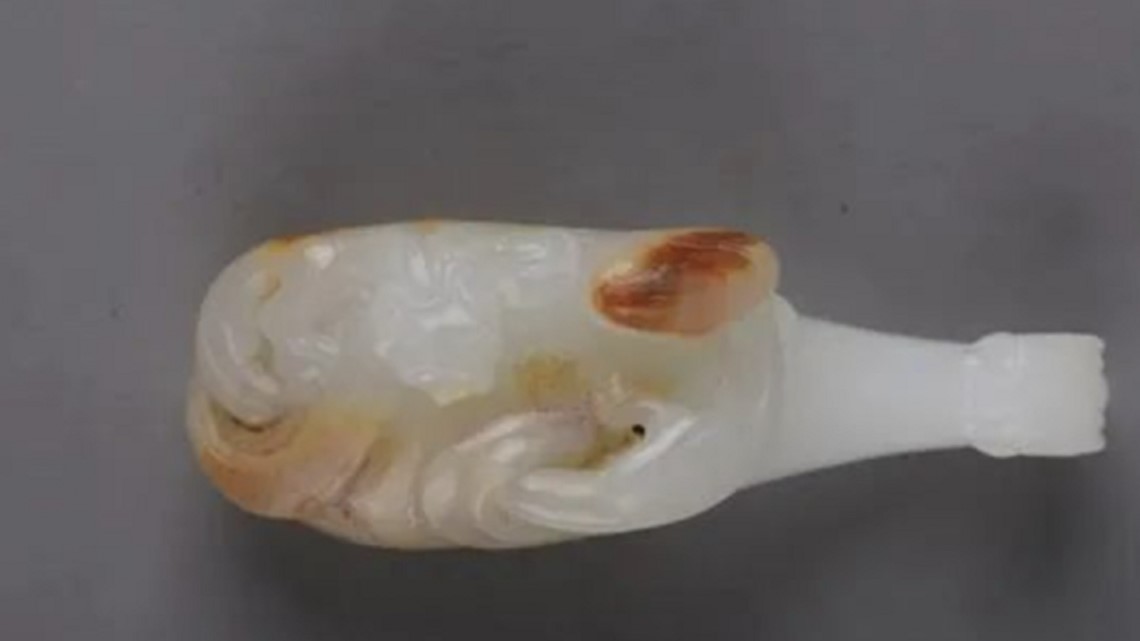
Using the dates of these artifacts and others found in the tombs, archaeologists were able to determine when in the dynasty the tombs were built. The largest tomb was likely built first.
Research in the area will continue, according to the news release. There was no information found about the tomb owners or those buried there, so archaeologists said they will try to determine who might have owned the cemetery and unveil "more historical mysteries."




