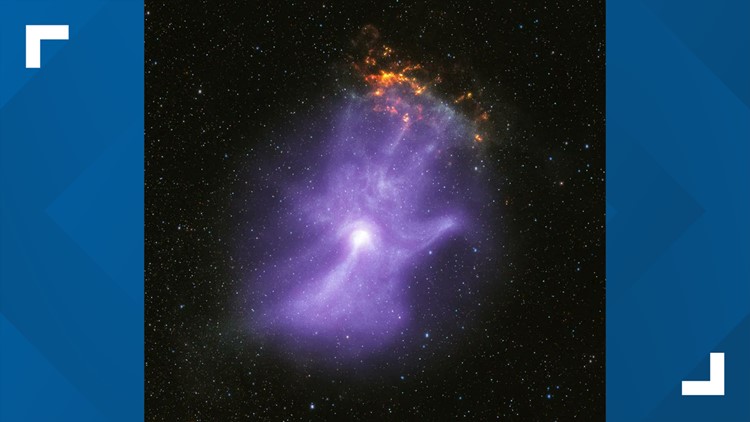
WASHINGTON — NASA has released a spooky new image that the space agency says shows the "bones" of a "ghostly cosmic hand."
The hand is actually the remnants of a collapsed giant star, which ran out of nuclear fuel around 1,500 years ago, NASA said in a news release, and is about 16,000 light-years from Earth. After collapsing, it became a dense neutron star. These neutron stars rotate and have strong magnetic fields called pulsars that create intense conditions that cannot be replicated elsewhere.
By focusing two of NASA's X-ray space telescopes on this neutron star and its surrounding magnetic fields, the agency and its astronomers are able to learn more about how a pulsar injects particles into space and shapes the environment surrounding the star. It's one of those pulsars that created the hand-shaped structure: X-ray data showed that a young pulsar created a jet of matter and antimatter that moved from the poles of the magnetic field to form a "pulsar wind nebula."
The nebula in this neutron star is known as MSH 15-52, and resembles a human hand. In the image, the pulsar is the "palm" of the hand, with five ghostly "fingers" stretching on.
NASA's Imaging X-Ray Polarimetry Explorer telescope studied the nebula for about 17 days, the agency said, marking the longest time it has focused on one object since its launch in Dec. 2021. That provided a map of the magnetic field, according to an astronomer who led the study.
"The IXPE data gives us the first map of the magnetic field in the 'hand'," said study leader Roger Romani of Stanford University in California. "The charged particles producing the X-rays travel along the magnetic field, determining the basic shape of the nebula, like the bones do in a person's hand."
Researchers said that in the nebula, there is a "remarkably high" amount of polarization, which likely means that the magnetic field is "very straight and uniform," with little turbulence in much of the nebula. The results also imply that the particles in the nebula that are in turbulent areas are given an "energy boost," causing them to flow to the "wrist, fingers and thumb" parts of the nebula.
"We've uncovered the life history of super energetic matter and antimatter particles around the pulsar," said study co-author Niccolò Di Lalla, also of Stanford. "This teaches us about how pulsars can act as particle accelerators."
The "ghostly cosmic hand" image was released just days after NASA announced its Juno mission had spotted an eerie "face" on Jupiter.